Carotid ultrasound is a cornerstone of vascular imaging, offering a non-invasive way to assess blood flow and detect stenosis before it leads to serious complications like stroke. Whether you’re a seasoned sonographer or refining your vascular scanning skills, mastering the nuances of how to perform a carotid ultrasound is crucial for accuracy and clinical relevance.
Carotid ultrasound is a cornerstone of vascular imaging, offering a non-invasive way to assess blood flow and detect stenosis before it leads to serious complications like stroke. Whether you’re a seasoned sonographer or refining your vascular scanning skills, mastering the nuances of how to perform a carotid ultrasound is crucial for accuracy and clinical relevance.
In this guide, we’ll walk through best practices for carotid artery imaging, common pitfalls, and interpretation essentials to help you achieve precise, reproducible results.
Why Carotid Ultrasound Matters
Carotid duplex ultrasound is widely used to evaluate:
✔ Carotid artery stenosis – Identifying narrowing due to atherosclerosis
✔ Plaque characteristics – Differentiating between stable and vulnerable plaques
✔ Stroke risk assessment – Detecting hemodynamically significant lesions
✔ Post-intervention monitoring – Following up on stents or endarterectomy outcomes
Without a doubt, this exam’s critical role in stroke prevention, understanding the best scanning techniques and interpretation criteria, is essential for accurate diagnosis and patient management.
Step-by-Step Best Practices for Carotid Ultrasound
1. Patient Positioning & Preparation
- First, position the patient supine with the head slightly extended and turned away from the scanning side.
- Use a high-frequency linear transducer (7-12 MHz) for optimal resolution. A low frequency curvilinear transducer might be helpful for deep vessels.
- Apply adequate but not excessive gel to ensure smooth transducer movement without air gaps.
- Remind the patient (kindly) that talking while the transducer is on the neck will interfere with the exam due to noise vibrations.
- Additionally, make sure to watch your positioning as well for proper ergonomics. Some sonographers sit behind the patient so they work in front of their body, not off to the side, putting stress on the shoulder.
2. Optimizing B-Mode Imaging for Anatomy & Plaque Assessment
- Begin with a gray-scale (B-mode) sweep from the clavicle to the mandible to identify the CCA, ICA, and ECA.
- Identify abnormalities, noting tortuosity, dissection, stenosis, occlusion, FMD, CBT, or aneurysm.
- Adjust gain and dynamic range to highlight echogenicity differences in soft, fibrous, and calcified plaques.
- Include transverse & longitudinal grayscale imaging. Use machine tools to measure the percent stenosis.
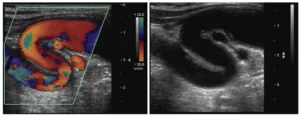 Tortuous carotid artery. It may feel like a pulsatile mass upon palpation.
Tortuous carotid artery. It may feel like a pulsatile mass upon palpation.
3. Identifying ICA vs. ECA (Internal vs. External Carotid Artery)
A common challenge is distinguishing the ICA from the ECA, especially in tortuous anatomy. Here’s how:
✅ ICA is usually posterior and has a larger, low-resistive, continuous waveform
✅ ECA is anterior, smaller in diameter, and shows a higher-resistance waveform with dicrotic notch
✅ ECA has visible branches, while ICA does not
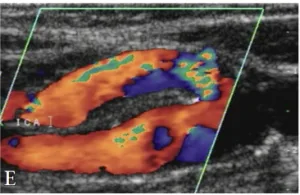
4. Doppler Optimization for Flow Analysis
- Angle correction is critical – Keep the Doppler angle ≤ 60° to ensure accurate velocity measurements.
- Avoid over-gaining Doppler settings, which can falsely elevate velocities.
- Sample midstream in the vessel, avoiding walls to prevent erroneous readings.
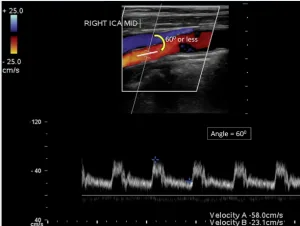
5. Common Pitfalls to Avoid
🚫 Improper Angle Correction – Over- or under-estimating angles can drastically alter velocity measurements.
🚫 Inadequate Sweep Speed – A slow sweep is ideal for detecting subtle plaque or turbulent flow.
🚫 Ignoring Post-Stenotic Turbulence – Always assess beyond the stenosis for flow disturbances.
Basic Carotid Protocol Images
Keep in mind that every image should be bilateral. Include grayscale longitudinal & transverse images, longitudinal color & pulsed Doppler images, and measure the PSV and EDV at each location.
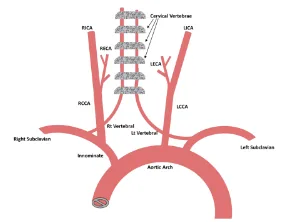
- CCA Proximal
- CCA Distal
- ICA Proximal
- Bulb
- ICA Mid
- ICA Distal
- ECA Proximal
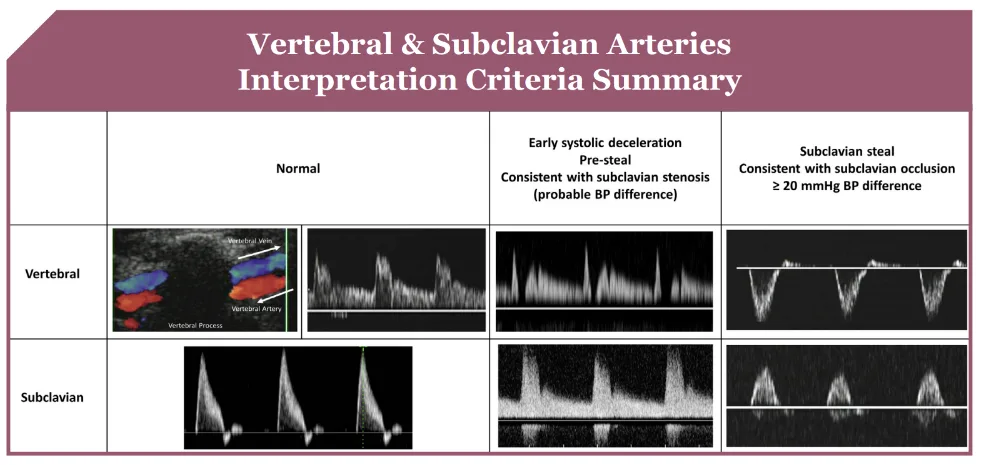
- Vertebral Artery
- Subclavian Artery
Carotid Stenosis Interpretation Criteria
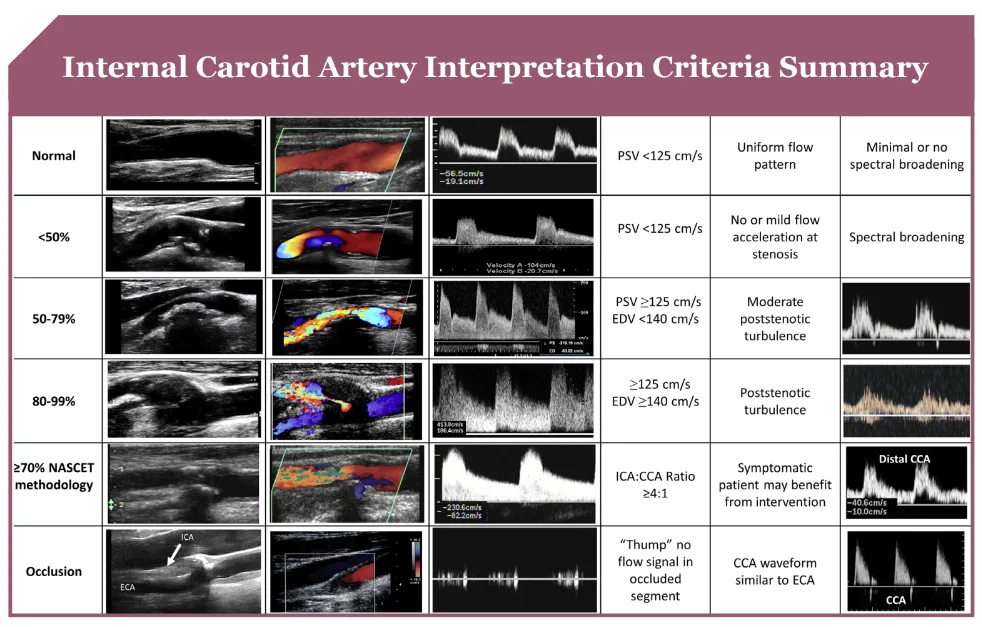
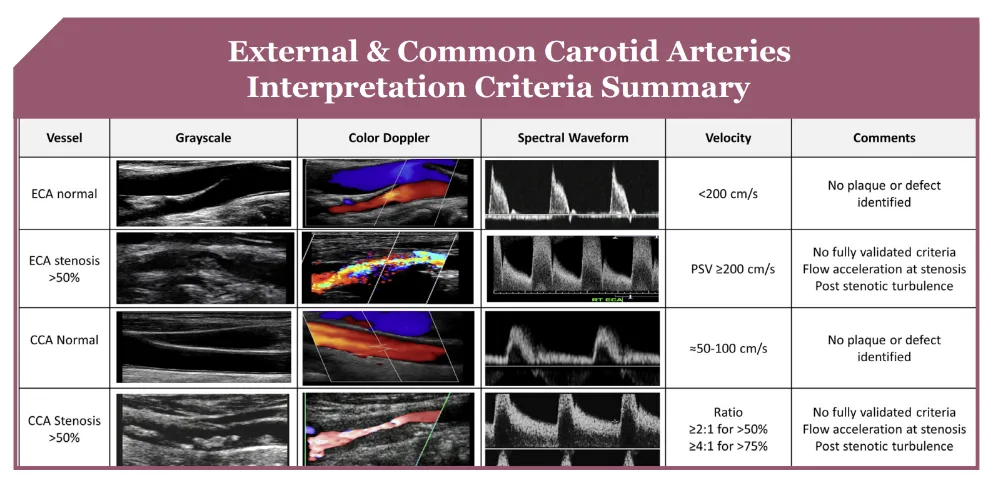
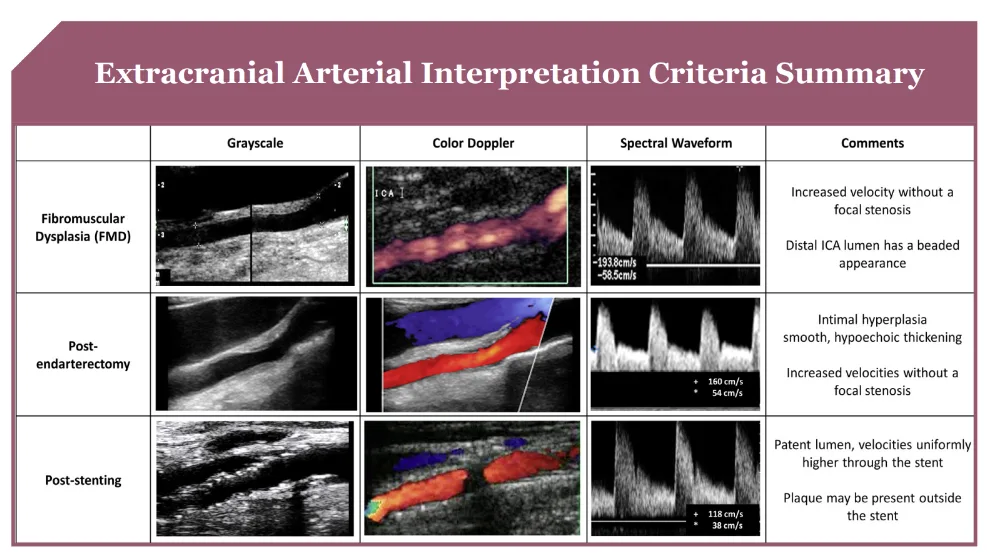
Enhance Your Expertise with The Art of Vascular Ultrasound
Mastering carotid ultrasound requires more than just knowing the protocols—it demands an understanding of how to interpret findings accurately and apply them clinically.
All of the information in this blog and more can be found in ESP’s newest book, The Art of Vascular Ultrasound, written by Jean White-Melendez and Bill Schroedter, ESP’s vascular registry review instructors!
📖 The Art of Vascular Ultrasound offers in-depth insights into:
✅ Real-world case studies that reinforce interpretation techniques
✅ Detailed illustrations and step-by-step scanning guides
✅ Essential Doppler criteria and common diagnostic challenges
🔗 Explore the Book Here (look through a flipbook and watch an interview with the authors!)
Refining your scanning techniques and applying structured interpretation criteria will improve diagnostic accuracy and deliver more confident vascular assessments.
To wrap up, carotid ultrasound remains one of the most valuable and widely used diagnostic tools in vascular imaging. By focusing on proper technique, avoiding common errors, and following evidence-based interpretation criteria, you can provide precise and reliable assessments that aid in stroke prevention and vascular health management.
At ESP’s core, we believe we are building confidence, developing understanding, and enhancing knowledge to provide better care for others. We hope you agree and join us in your educational journey